nursing diagnosis
nursing diagnosis

- A nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment about individual, family, or community experiences and responses to actual or potential health problems or life processes. It may be part of the nursing process. In contrast to dependent interventions driven by physician orders (such as medication administration), nursing diagnoses encourage the nurse’s independent practice (such as patient comfort or relief). The information gathered during the nursing assessment is used to make nursing diagnoses. A problem response that was present at the time of assessment is presented in a problem-based nursing diagnosis. Health promotion diagnoses identify areas that can be improved to improve health, whereas risk diagnoses represent vulnerabilities to potential issues. A nursing diagnosis identifies the unique ways in which individuals respond to health or life processes or crises, whereas a medical diagnosis identifies a disorder. Among other diagnostic procedures, the nursing process is unique. When possible, a nursing diagnosis incorporates patient involvement throughout the process. An official taxonomy of nursing diagnosis is developed, researched, and refined by NANDA International (NANDA-I), a group of professionals.
- To get the most out of their jobs, all nurses need to be familiar with the steps in the nursing process. During the assessment, the nurse must draw quick and precise conclusions from the patient’s data in order to make a correct diagnosis. These conclusions must be based on knowledge of the nursing field and concepts that are important to nurses.
Purposes of Nursing Diagnosis
The nursing diagnosis serves the following purpose:
- assists in determining nursing priorities and directing nursing interventions in accordance with those priorities.
assists in the formulation of expected outcomes for third-party payer quality assurance requirements.
Diagnoses made by nurses assist in determining a client’s or group’s response to actual or potential health and life processes, as well as their strengths and resources that can be utilized to prevent or resolve issues.
serves as a foundation for understanding and communication between nursing professionals and the healthcare team and serves as a common language.
serves as the foundation for evaluating whether the client received cost-effective and beneficial nursing care.
Nursing diagnoses are a useful teaching tool for improving students’ critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Classification of Nursing Diagnoses (Taxonomy II)
How are nursing diagnoses categorized, listed, or arranged? Based on Dr. Mary Joy Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns assessment framework, Taxonomy II was adopted in 2002. There are three levels in Taxonomy II: thirteen domains, 47 classes, and nursing diagnoses. Diagnoses in nursing are now coded according to seven axes rather than Gordon’s patterns: descriptor, topology, age, health status, diagnostic concept, and unit of care Additionally, instead of being listed by first word, diagnoses are now listed alphabetically by the concept.
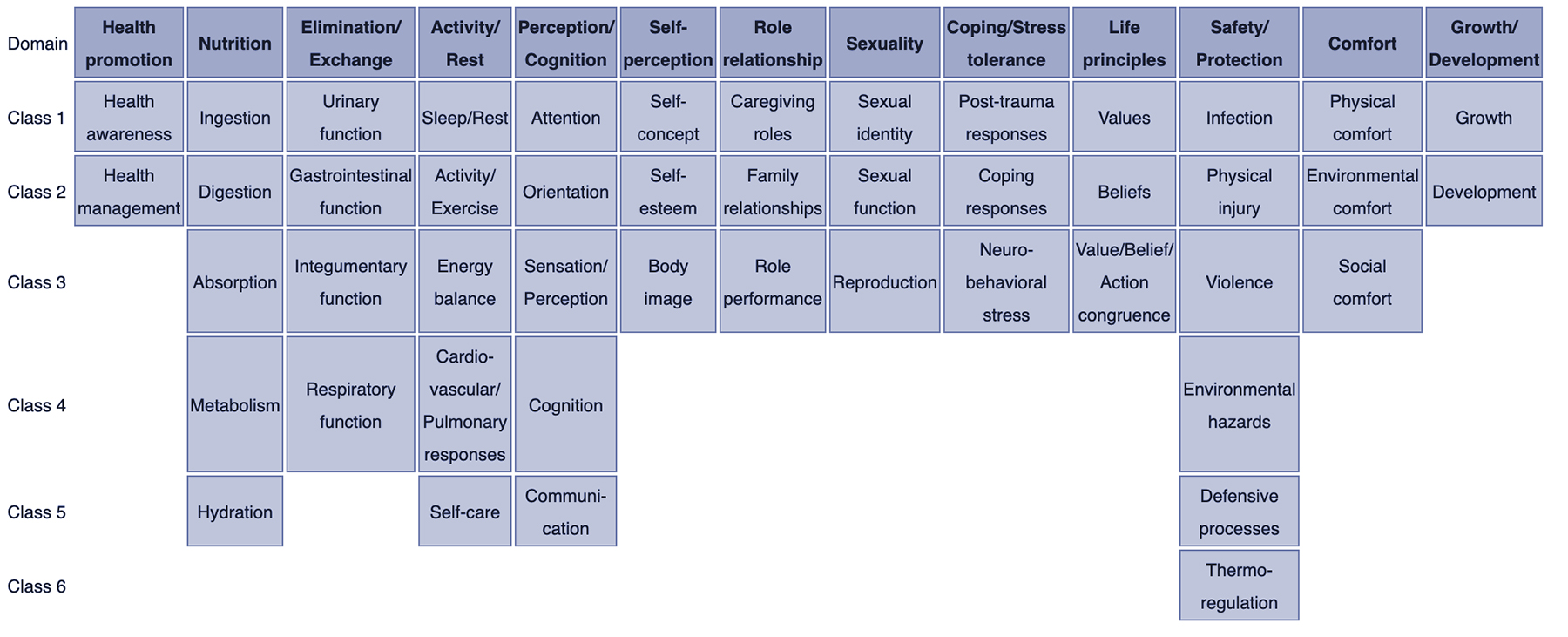
- Domain 1. Health Promotion
- Class 1. Health Awareness
- Class 2. Health Management
- Domain 2. Nutrition
- Class 1. Ingestion
- Class 2. Digestion
- Class 3. Absorption
- Class 4. Metabolism
- Class 5. Hydration
- Domain 3. Elimination and Exchange
- Class 1. Urinary function
- Class 2. Gastrointestinal function
- Class 3. Integumentary function
- Class 4. Respiratory function
- Domain 4. Activity/Rest
- Class 1. Sleep/Rest
- Class 2. Activity/Exercise
- Class 3. Energy balance
- Class 4. Cardiovascular/Pulmonary responses
- Class 5. Self-care
- Domain 5. Perception/Cognition
- Class 1. Attention
- Class 2. Orientation
- Class 3. Sensation/Perception
- Class 4. Cognition
- Class 5. Communication
- Domain 6. Self-Perception
- Class 1. Self-concept
- Class 2. Self-esteem
- Class 3. Body image
- Domain 7. Role relationship
- Class 1. Caregiving roles
- Class 2. Family relationships
- Class 3. Role performance
- Domain 8. Sexuality
- Class 1. Sexual identity
- Class 2. Sexual function
- Class 3. Reproduction
- Domain 9. Coping/stress tolerance
- Class 1. Post-trauma responses
- Class 2. Coping responses
- Class 3. Neurobehavioral stress
- Domain 10. Life principles
- Class 1. Values
- Class 2. Beliefs
- Class 3. Value/Belief/Action congruence
- Domain 11. Safety/Protection
- Class 1. Infection
- Class 2. Physical injury
- Class 3. Violence
- Class 4. Environmental hazards
- Class 5. Defensive processes
- Class 6. Thermoregulation
- Domain 12. Comfort
- Class 1. Physical comfort
- Class 2. Environmental comfort
- Class 3. Social comfort
- Domain 13. Growth/Development
- Class 1. Growth
- Class 2. Development
Components of a Nursing Diagnosis
There are typically three components to a nursing diagnosis: 1) the problem and its definition, 2) the cause, and 3) the characteristics or risk factors that define it (for risk diagnosis).
Click here for South African Nursing Colleges and Schools Application 2023-2024
RELATED LINKS
Nursing Online Application links
